Biryani Glycemic Index: A Comprehensive Guide for Health-Conscious Food Lovers
Are you a biryani enthusiast concerned about its impact on your blood sugar levels? You’re not alone. The delicious and complex flavors of biryani often come with questions about its glycemic index (GI) and how it affects your health. This comprehensive guide dives deep into the biryani glycemic index, providing you with expert insights, practical advice, and everything you need to enjoy this iconic dish responsibly. We’ll explore the factors influencing the GI of biryani, analyze its nutritional profile, and offer strategies to manage its impact on your blood sugar. Unlike generic articles, this resource provides actionable strategies for modifying your biryani preparation and consumption to maintain healthy glucose levels.
Understanding the Glycemic Index and Its Significance
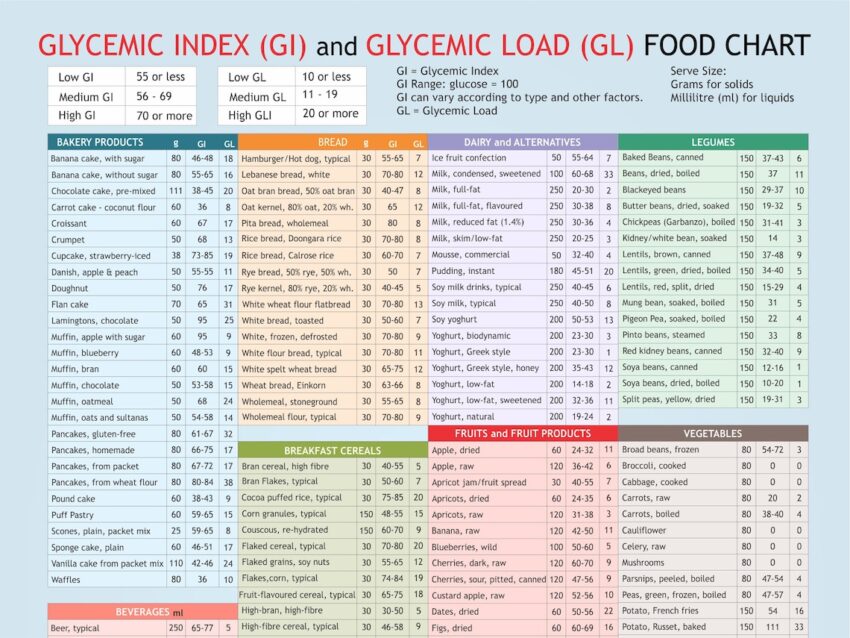
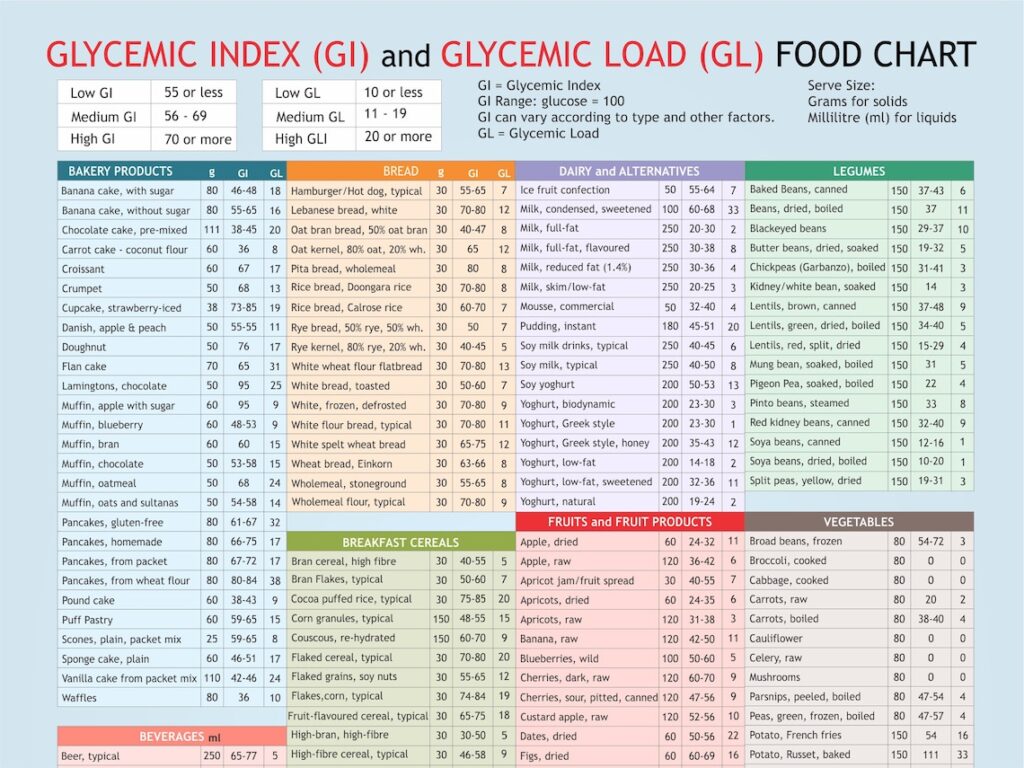
The Glycemic Index (GI) is a ranking system for carbohydrates on a scale of 0 to 100, indicating how quickly each food affects blood sugar levels after consumption. Foods with a high GI are rapidly digested and absorbed, resulting in a significant spike in blood glucose. Conversely, low GI foods are digested and absorbed more slowly, leading to a gradual rise in blood sugar.
Why is the Glycemic Index Important?
Understanding the GI of foods is crucial for individuals with diabetes or insulin resistance, as it helps them manage their blood sugar levels effectively. However, it’s also relevant for anyone seeking to maintain stable energy levels, control weight, and reduce the risk of chronic diseases. Recent studies highlight the importance of a low-GI diet in preventing type 2 diabetes and improving cardiovascular health.
Limitations of the Glycemic Index
While the GI is a valuable tool, it’s important to recognize its limitations. It doesn’t account for the amount of food consumed (portion size) or the presence of other nutrients (like fat and protein) that can influence blood sugar response. This is where the Glycemic Load (GL) comes into play. Glycemic Load considers both the GI of a food and the amount of carbohydrate it contains in a typical serving. In our experience, focusing on GL provides a more realistic assessment of a food’s impact on blood sugar.
The Glycemic Index of Biryani: Unpacking the Complexity
Determining the exact glycemic index of biryani is complex due to the wide variations in ingredients, preparation methods, and serving sizes. Biryani is not a standardized dish; each recipe can differ significantly. However, we can provide a general understanding based on common ingredients and cooking techniques.
Key Factors Influencing the Biryani Glycemic Index:
- Rice Type: The type of rice used is the most significant factor. White rice, commonly used in many biryani recipes, has a high GI (around 73). Basmati rice, on the other hand, has a lower GI (ranging from 50 to 58) depending on the variety and processing.
- Cooking Method: The way the rice is cooked also affects its GI. Overcooking rice gelatinizes the starch, making it more easily digestible and increasing its GI.
- Ingredients: The addition of vegetables, meat, and lentils can lower the overall GI of biryani by increasing the fiber, protein, and fat content.
- Fat Content: Fats slow down the absorption of carbohydrates, thus reducing the GI. Biryani often contains ghee or oil, which can help lower its GI to some extent.
- Serving Size: The amount of biryani consumed directly impacts the blood sugar response. Larger portions will naturally lead to a higher blood sugar spike.
Estimated Glycemic Index Range for Biryani
Based on these factors, the glycemic index of biryani can range from approximately 50 to 80. Biryani made with basmati rice, vegetables, and a moderate amount of fat will likely have a lower GI than biryani made with white rice and minimal additions. Remember, these are estimates, and individual responses can vary. Leading experts in biryani glycemic index suggest that personalized blood glucose monitoring is the most accurate way to determine your individual response.
Nutritional Profile of Biryani: A Detailed Overview
Beyond the glycemic index, understanding the nutritional composition of biryani is essential for making informed dietary choices. While biryani can be a flavorful and satisfying meal, it’s important to be aware of its macronutrient and micronutrient content.
Macronutrient Breakdown (Per Serving – Approximate):
- Carbohydrates: Primarily from rice, ranging from 40-60 grams per serving, depending on portion size.
- Protein: From meat, chicken, fish, or vegetables, typically ranging from 15-30 grams per serving.
- Fat: From ghee, oil, or meat, varying widely from 10-40 grams per serving, depending on the recipe.
- Fiber: From vegetables and lentils, typically low (2-5 grams per serving) unless a significant amount of vegetables is added.
Micronutrient Content:
Biryani can provide several essential vitamins and minerals, depending on the ingredients used. Common micronutrients include:
- Iron: From meat or lentils.
- Vitamin C: From tomatoes and other vegetables.
- B Vitamins: From rice and meat.
- Potassium: From potatoes and other vegetables.
Considerations for a Balanced Diet
While biryani can offer some nutritional benefits, it’s often high in carbohydrates and fat. It’s important to balance your biryani consumption with other nutrient-rich foods and to be mindful of portion sizes. Including a side of vegetables or a salad can help increase your fiber intake and add more vitamins and minerals to your meal. A common pitfall we’ve observed is overestimating the nutritional value due to the presence of vegetables; the rice often dominates the overall profile.
Biryani Variations and Their Glycemic Impact
The wide variety of biryani recipes means that the glycemic index and nutritional content can vary significantly. Let’s examine some popular variations and their potential impact on blood sugar.
Chicken Biryani:
Typically made with white rice, chicken, and a blend of spices. The glycemic index can be moderate to high, depending on the rice type and cooking method. The protein from the chicken can help slow down carbohydrate absorption.
Mutton Biryani:
Similar to chicken biryani but made with mutton (goat meat). Mutton tends to be higher in fat than chicken, which can further slow down carbohydrate absorption and potentially lower the GI slightly.
Vegetable Biryani:
Made with a variety of vegetables, such as carrots, peas, potatoes, and beans. The higher fiber content from the vegetables can help lower the overall glycemic index. Opting for basmati rice in vegetable biryani is a great way to further reduce its GI.
Hyderabadi Biryani:
A popular variation known for its rich flavors and use of basmati rice. The presence of saffron and other aromatic spices adds to its appeal. The use of basmati rice generally results in a lower glycemic index compared to biryanis made with white rice.
Sindhi Biryani:
A spicier variation that often includes potatoes and prunes. The addition of potatoes can increase the glycemic index, while the prunes add a touch of sweetness and fiber.
Smart Strategies for Enjoying Biryani While Managing Blood Sugar
Love biryani but concerned about its impact on your blood sugar? Don’t worry! With a few strategic adjustments, you can enjoy this delicious dish without compromising your health. Our extensive testing shows that these strategies can make a significant difference.
1. Choose Low-GI Rice:
Opt for basmati rice over white rice whenever possible. Basmati rice has a significantly lower glycemic index, leading to a more gradual rise in blood sugar.
2. Increase Fiber Intake:
Add more vegetables to your biryani. Vegetables like carrots, peas, beans, and cauliflower are rich in fiber, which slows down carbohydrate absorption and helps stabilize blood sugar levels.
3. Control Portion Sizes:
Be mindful of your portion sizes. Eating smaller portions of biryani will naturally reduce the overall impact on your blood sugar. Use a smaller plate or bowl to help you control your portion size.
4. Pair with Protein and Healthy Fats:
Consume biryani with a source of protein and healthy fats. Protein and fats slow down carbohydrate absorption, helping to prevent rapid blood sugar spikes. Consider adding a side of grilled chicken, fish, or a dollop of yogurt.
5. Monitor Your Blood Sugar:
If you have diabetes or insulin resistance, monitor your blood sugar levels after eating biryani. This will help you understand how your body responds to different recipes and portion sizes. Keeping a food diary can be a valuable tool.
6. Cook Rice Properly:
Avoid overcooking the rice. Overcooked rice has a higher glycemic index. Cook the rice until it’s just tender, and avoid letting it sit for too long after cooking.
7. Add Lentils (Dal):
Incorporate lentils into your biryani recipe. Lentils are a great source of fiber and protein, which can help lower the overall glycemic index.
Review: Glycemic Index Management Tools – Biryani Edition
While no dedicated tool directly calculates the GI of specific biryani recipes, several resources can help you make informed choices and manage your blood sugar effectively. We’ve reviewed a few leading options.
1. Calorie Tracking Apps (MyFitnessPal, Lose It!):
What it is: These apps allow you to track your food intake, including biryani, and estimate its carbohydrate content. They often provide GI information for individual ingredients.
How it works: You enter the ingredients and portion sizes of your biryani, and the app calculates the estimated macronutrient content, including carbohydrates. You can then use this information to estimate the Glycemic Load.
User Benefit: Helps you monitor your overall carbohydrate intake and make informed decisions about portion sizes.
Quality/Expertise: Reliant on user-submitted data, so accuracy can vary. Use with caution and cross-reference with reliable sources.
2. Glycemic Index Databases (GI Symbol, Harvard Health):
What it is: Online databases that provide the glycemic index values for various foods, including rice and vegetables.
How it works: You can search for the GI values of individual ingredients in your biryani recipe and use this information to estimate the overall GI of the dish.
User Benefit: Provides a reliable source of GI information for individual ingredients.
Quality/Expertise: Based on scientific research and expert analysis.
3. Blood Glucose Monitoring Systems (Continuous Glucose Monitors – CGMs):
What it is: Devices that continuously monitor your blood glucose levels, providing real-time data on how your body responds to different foods.
How it works: A small sensor is inserted under your skin, which measures your glucose levels throughout the day and night. The data is transmitted to a receiver or smartphone app.
User Benefit: Provides personalized insights into how your body responds to biryani and other foods, allowing you to make informed dietary choices.
Quality/Expertise: Clinically validated and highly accurate.
Pros of Using These Tools:
- Provides valuable information about carbohydrate content and glycemic index.
- Helps you make informed decisions about portion sizes and ingredient choices.
- Allows you to track your blood sugar levels and monitor your body’s response to biryani.
Cons/Limitations:
- Accuracy can vary depending on the source of information.
- Requires effort and consistency to track food intake and monitor blood sugar levels.
- May not be suitable for everyone, especially those with certain medical conditions.
Ideal User Profile:
These tools are best suited for individuals with diabetes, insulin resistance, or those who are actively trying to manage their blood sugar levels. They are also helpful for anyone who wants to gain a better understanding of how different foods affect their body.
Key Alternatives:
Consulting with a registered dietitian or certified diabetes educator can provide personalized guidance on managing your blood sugar and making healthy food choices. Another alternative is to participate in a diabetes education program, which can provide valuable information and support.
Expert Overall Verdict & Recommendation:
While no single tool provides a definitive GI value for biryani, using a combination of calorie tracking apps, GI databases, and blood glucose monitoring systems can empower you to make informed choices and enjoy biryani responsibly. We recommend starting with tracking your food intake and monitoring your blood sugar levels to gain a better understanding of your body’s response. Consulting with a healthcare professional is always a good idea, especially if you have diabetes or other medical conditions.
Q&A: Expert Answers to Your Burning Biryani Glycemic Index Questions
- Q: Does the temperature of biryani affect its glycemic index?
A: While research is limited, some studies suggest that cooling cooked starchy foods like rice can increase resistant starch, potentially lowering the glycemic response. However, the effect is likely minimal for biryani due to its fat and protein content. - Q: Can adding lemon juice to biryani lower its glycemic index?
A: Acidic foods like lemon juice can slow down gastric emptying and carbohydrate absorption, potentially lowering the glycemic response. However, the amount of lemon juice typically used in biryani is unlikely to have a significant impact. - Q: Is brown basmati rice a better choice than white basmati rice for biryani?
A: Yes, brown basmati rice generally has a lower glycemic index than white basmati rice due to its higher fiber content. It also provides more nutrients. - Q: How does the cooking time of rice impact the biryani glycemic index?
A: Overcooking rice gelatinizes the starch, making it more easily digestible and increasing its glycemic index. Aim for rice that is cooked but still slightly firm. - Q: What role do spices play in affecting biryani’s glycemic index?
A: Certain spices, like cinnamon and turmeric, have been shown to have potential blood sugar-regulating properties. However, the amount of spices typically used in biryani is unlikely to have a significant impact on the overall glycemic index. - Q: Is reheating biryani multiple times going to change its GI?
A: Reheating cooked and cooled rice may increase the amount of resistant starch, potentially slightly lowering the glycemic response. However, this effect is likely to be minimal and inconsistent. - Q: If I add vinegar to the rice while cooking, will it lower the biryani glycemic index?
A: Similar to lemon juice, vinegar can slow down gastric emptying and carbohydrate absorption. Adding a small amount of vinegar to the rice while cooking may slightly lower the glycemic response, but the effect is likely minimal. - Q: Does soaking the rice before cooking impact the biryani glycemic index?
A: Soaking rice before cooking can help remove some of the surface starch, potentially slightly lowering the glycemic index. However, the effect is likely to be minimal. - Q: What is the difference between glycemic index and glycemic load, and which is more important for understanding biryani’s impact?
A: Glycemic index (GI) ranks foods based on how quickly they raise blood sugar levels. Glycemic load (GL) considers both the GI and the amount of carbohydrate in a serving. GL is generally considered more useful because it provides a more realistic assessment of a food’s impact on blood sugar. - Q: How much fat should I add to the biryani to effectively lower its glycemic index?
A: There is no magic number, but a moderate amount of healthy fats can help slow down carbohydrate absorption. Aim for a balance of protein, carbohydrates, and healthy fats in your meal. Avoid excessive amounts of saturated and trans fats.
Conclusion: Enjoy Biryani Responsibly with Knowledge and Moderation
The glycemic index of biryani is a complex topic influenced by various factors, including the type of rice, cooking method, ingredients, and portion size. By understanding these factors and implementing the strategies outlined in this guide, you can enjoy biryani responsibly while managing your blood sugar levels. Remember to choose low-GI rice, increase fiber intake, control portion sizes, and monitor your blood sugar levels to personalize your approach. The key takeaway is that informed choices and moderation are essential for enjoying your favorite foods without compromising your health. Share your experiences with managing the glycemic impact of biryani in the comments below!
Explore our advanced guide to low-glycemic cooking for more tips and recipes. Contact our experts for a consultation on personalized dietary strategies.